Eye Clinic Tokyo has prepared content that will help you to understand various eye diseases.
This time, it’s about retinal detachment.
■Retinal detachment
【Disease】
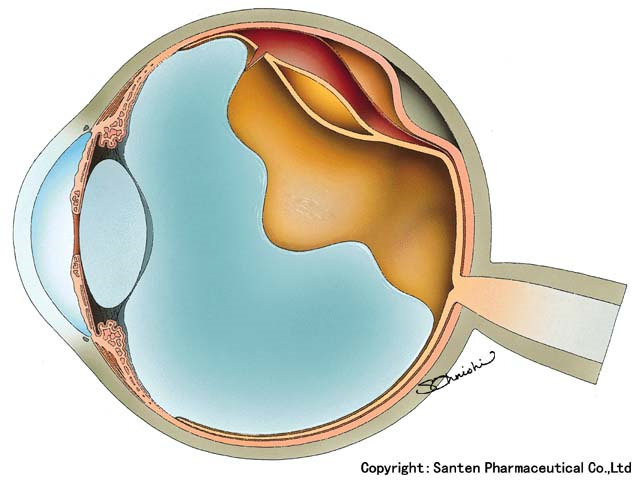
Retinal detachment describes an emergency situation in which a thin layer of tissue (the retina) at the back of the eye pulls away from its normal position.
The retina plays a role in sensing light and transmitting visual information to the brain, and if retinal detachment occurs, there is a risk of visual impairment, visual field disorder and vision loss.
Retinal detachment is a relatively rare eye disease, but its frequency varies depending on age and certain risk factors. The risk of retinal detachment increases with age. It is especially common in people over the age of 40, but in addition to aging, people with high myopia often have thinner retinas, increasing the risk of retinal detachment. The higher the power of myopia, the more likely the person is to develop it. In addition, genetic factors may be involved, such as if there is a family history of retinal detachment, or retinal detachment may be also triggered by retinal damage.

【Symptoms】
Retinal detachment itself is painless. But warning signs almost always appear before it occurs or has advanced, such as: the sudden appearance of many floaters — tiny specks that seem to drift through your field of vision, flashes of light in one or both eyes, blurred vision, gradually reduced side (peripheral) vision, a curtain-like shadow over your field of vision.


【Treatment】
Treatment is often vitrectomy. Surgery is generally performed under local anesthesia.
There is a treatment that injects air or gas into the eye where the retina is detached, and the gas enters the eye to help the detachment reattach to the wall of the eyeball. The patient is instructed to keep a specific position, the gas pushes the area of the retina containing the hole or holes against the wall of the eye. In this treatment, it is necessary to take a rest for about 2 to 6 weeks depending on the patient’s condition.
Except gas, there is another treatment, injecting silicone oil into the vitreous space to help flatten the retina, and silicone oil may be temporarily injected into the eye. The silicone oil stays in the eye for a long time but must be removed in another surgery at a later date. Depending on the patient’s age, cataract surgery may be performed at the same time as vitrectomy.
Vitreous surgery is not the only treatment for retinal detachment, but there is also a surgery called retinopexy for treatment of young people. This surgery is also basically performed under local anesthesia, but compared to vitrectomy surgery, it is more painful because the extraocular muscles are manipulated, so it is sometimes performed under general anesthesia.
In this surgery, a silicone sponge is sewn between the extraocular muscles and the sclera to fix the retina, so in case this affects the movement of the extraocular muscles cause double vision or misalignment of the eyes due to eye movement disorders, it is necessary to check your vision after surgery, such as double vision.
These treatments are determined by you depending on the severity of symptoms and the progress of retinal detachment. Proper rest and use of prescribed medications are important for recovery.
【Summary】
Retinal detachment is a disease that with early detection and treatment, and appropriate treatment can prevent vision decrease and vision loss. The important thing is to consult an ophthalmologist as soon as possible if the initial symptoms of retinal detachment appear and receive an appropriate diagnosis and early treatment according to the condition.
If treatment is delayed, it may cause various vision problems. It’s important to get early treatment.


